PON and GPON networks
The acronym PON, frequently used in fiber installations, comes from English. It stands for Passive Optical Network.
It is a passive network, with a single point of transmission to different user points. A PON network has no more active elements to reactivate the signal. The distribution is carried out by means of optical distributors or splitters. It is the topology used in FTTH installations (fiber to the home).
When the transmission speed is capable of ensuring 2.4Gbit/s at a distance of 20 km and 128 users, we say that we are dealing with a GPON network. And this is what, normally, we have in our homes.
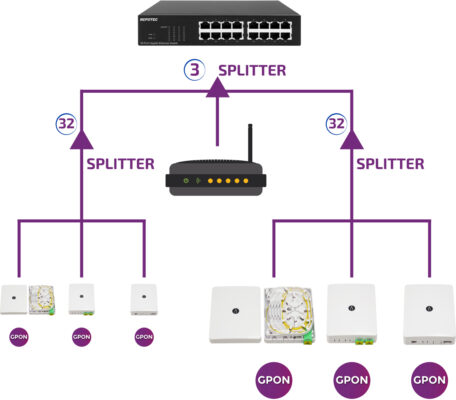
The basic elements of a PON or GPON network are:
- OLT (Optical Line Termination). It is the active element in the headend, from which the fibers depart towards the users.
- ONT (Optical Network Terminal) It is the element located at the end user’s home.
- DOPT, Optical dividers. Splitters.
- Fiber cable to interconnect the other elements
- WDM (Multiplexer) are passive elements responsible for combining or separating different wavelengths in a single fiber.
Keep in mind that the equipment is not universal, and the compatibility between OLT and ONT must be guaranteed.
GPON networks are bidirectional, although the maximum speeds are 2.5 Gbit/s from OLT to ONT, which is called downstream, and half, 1.25 Gbit/s from ONT to OLT, which is called upstream.
From OLT to ONT, the information is identical for all (Broadcast), while from ONT to OLT, the system assigns a time to each user to avoid any collisions. This system is called TDMA modulation.
GPON networks have multiple advantages over XSDL, which was used before:
- Distance up to 20Km.
- Bandwidth (2.4 Gbps and 1.2 Gbps).
- Quality of service, error less than 10EXP-10.
- Security: Encrypted information.
- Remote network management.
- There is no energy consumption, neither force nor batteries.
- Multiplexing of services through the same cable: Voice, Data, TV, Video on demand, Video RF, etc…
In addition to the traditional Gpon networks with cascading distribution boxes/splitters and where fibres are segregated and spliced, there is a new distribution system called Asymmetrical for which Keynet provides a number of solutions.
Basically it consists of using splitters that incorporate a directional coupler that splits the signal in an unbalanced way by applying a higher signal loss level to the distribution box present in order to have more signal to send to the next box and so successively.
This is a “plug & play” installation system that is very quick and safe to install by non highly qualified personnel. The Gpon asymmetric networks can be installed not only in towns but also in buildings.
The capacity to manage ONTs is the same in both symmetrical and asymmetrical networks.
